 Political Instability in Africa
Political Instability in Africa

This study was initially commissioned by the African Telematics program at
CIDCM (University of Maryland), with funding from USAID, in order to better
understand the sources and drivers of instability in African countries and the
crucial role of communications technologies in development and stabilization
processes. The results of the study were originally published in Section 7,
"Focus on Political Instability in Africa," Peace and Conflict
2005 and further elaborated in a special report commissioned by the UK Department
for International Development (DfID) titled, Conflict Trends in Africa, 1946-2004
(electronic copies of both publications are available from the CSP Virtual Library,
click here). The basis
for the analysis is the demarcation of periods of stability, state formation
instability, and post-formation instability for each country in Africa.
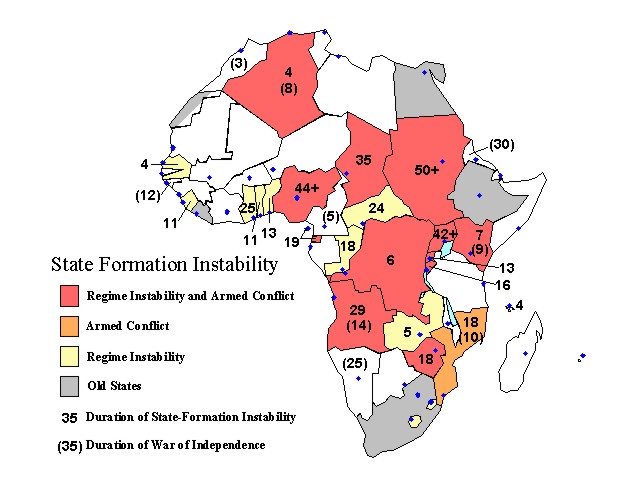
The individual country plots of instability events and the demarcation of periods
of stability and instability are posted here as support documentation for the
reported analysis and findings. The diagram below reproduces figure 7.4 from
the Peace and Conflict 2005 report and charts the general condition of
African countries as they gain independence during the post-World War II "decolonization"
period; only four countries in Africa gained independence in the modern state
system prior to 1946 (Egypt, Ethiopia, Liberia, and South Africa). To
view the individual country plots of political instability events and the periods
of stability and instability demarcated for the Africa study, click on a country
in the map below. Note: The blue dots in the diagram below
locate the capital city in each country. The territory of the former-Spanish
Sahara, presently claimed by Morocco, is not included in the analyses.

|
 Political Instability in Africa
Political Instability in Africa